Cloud Data Warehouse
Cloud Data Warehouse
The advantage of the cloud is infinite compute and infinite storage. Cloud-native data warehouse systems also allow for serverless workflows that can integrate Machine Learning directly on the data lake.
GCP Big Query
There is a lot to like about GCP Big Query. It is serverless, it has integrated Machine Learning, and it is easy to use. This next section has a walkthrough of a k-means clustering tutorial.
The interface when queried gives back results in an intuitive fashion.

SCREENCAST of K-Means Walkthrough:
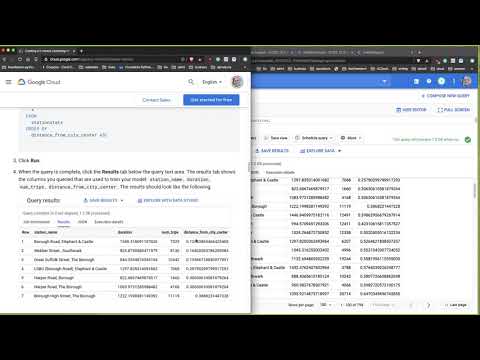
Note, how a SQL statement can actually train the model. The kmeans section is where the magic happens.
CREATE OR REPLACE MODEL
bqml_tutorial.london_station_clusters OPTIONS(model_type='kmeans',
num_clusters=4) AS
WITH
hs AS (
SELECT
h.start_station_name AS station_name,
IF
(EXTRACT(DAYOFWEEK
FROM
h.start_date) = 1
OR EXTRACT(DAYOFWEEK
FROM
h.start_date) = 7,
"weekend",
"weekday") AS isweekday,
h.duration,
ST_DISTANCE(ST_GEOGPOINT(s.longitude,
s.latitude),
ST_GEOGPOINT(-0.1,
51.5))/1000 AS distance_from_city_center
FROM
`bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_hire` AS h
JOIN
`bigquery-public-data.london_bicycles.cycle_stations` AS s
ON
h.start_station_id = s.id
WHERE
h.start_date BETWEEN CAST('2015-01-01 00:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP)
AND CAST('2016-01-01 00:00:00' AS TIMESTAMP) ),
stationstats AS (
SELECT
station_name,
isweekday,
AVG(duration) AS duration,
COUNT(duration) AS num_trips,
MAX(distance_from_city_center) AS distance_from_city_center
FROM
hs
GROUP BY
station_name, isweekday)
SELECT
* EXCEPT(station_name, isweekday)
FROM
stationstats
Finally, when the k-means cluster it is trained, the evaluation metrics can be analyzed.

Often a great final step is to then take the result and export it to their Business Intelligence (BI) tool, data studio.

Summary of GCP Big Query
- Serverless
- Large selection of Public Datasets
- Integrated Machine Learning
- Integration with Data Studio
- Intuitive
- SQL based
AWS Redshift
SCREENCAST of K-Means Walkthrough:
Key actions in a Redshift Workflow
In general the key actions are as described in the Redshift getting started guide are:
- Cluster Setup
- IAM Role configuration (what can role do?)
-
Setup Security Group (i.e. open port 5439)
- Setup Schema
create table users( userid integer not null distkey sortkey, username char(8), - Copy data from S3
copy users from 's3://awssampledbuswest2/tickit/allusers_pipe.txt'
credentials 'aws_iam_role=<iam-role-arn>'
delimiter '|' region 'us-west-2';
- Query
SELECT firstname, lastname, total_quantity
FROM
(SELECT buyerid, sum(qtysold) total_quantity
FROM sales
GROUP BY buyerid
ORDER BY total_quantity desc limit 10) Q, users
WHERE Q.buyerid = userid
ORDER BY Q.total_quantity desc;
Summary of AWS Redshift
- Mostly managed
- Deep Integration with AWS
- Columnar
- Competitor to Oracle and GCP Big Query
- Predictable performance on huge datasets